Annealing is a heat therapy process that entails home heating a material to a particular temperature where atomic flexibility increases, permitting for the alleviation of internal stresses, decrease of firmness, and enhancement of ductility. This procedure efficiently alters the microstructural structure of the metal, permitting the setup of atoms to redistribute themselves right into a state of lower energy. Usual steels undergoing annealing consist of light weight aluminum, steel, and copper, where the variants of annealing-- such as complete annealing, process annealing, and spheroidizing-- generate various results based on the details demands of the application.
In comparison, normalizing is likewise a heat treatment procedure but is mainly used to fine-tune the grain framework of a metal and attain an attire and wanted mechanical home throughout. The procedure benefits from a greater cooling rate, which affects the final microstructure, resulting in a finer and even more uniform plan of grains contrasted to metals treated with annealing. It is a particularly effective treatment for ferrous alloys, such as carbon steels, where achieving high-performance product buildings like yield stamina and tensile toughness is frequently needed for industrial applications.
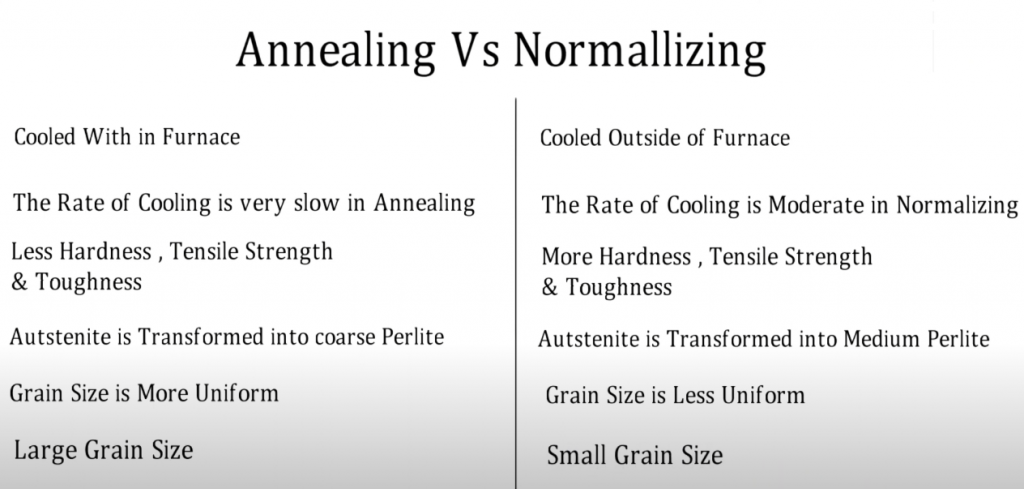
Explore annealed vs normalized the vital distinctions in between annealing and normalizing in metallurgy, 2 essential heat treatment procedures that considerably affect the mechanical buildings and performance of steels and alloys in numerous applications.
While both processes share similarities, they are selected based on the certain residential properties required for a classification or application of the product. In making procedures where enhanced mach inability, good formability, or improved ductility is desirable, products are much more likely to go through annealing.
Throughout numerous sectors, annealing and stabilizing offer substantial roles. As an example, in the automobile industry, while lots of elements are produced with creating or casting, subsequent heat treatments are essential. Annealing is often utilized for steel parts, such as gears and shafts, to improve resistance versus weak fracturing, which might develop from welding procedures or functional stress throughout their life span. Likewise, normalizing finds extensive applications in structural parts for structures and equipment, where the enhancement of mechanical residential or commercial properties under loading conditions is of utmost importance. This microstructural improvement promotes enhancements in yield strength and sturdiness, consequently prolonging the lifespan and efficiency capacities of these products.
Both warmth therapy processes additionally highlight the equilibrium between achieving wanted physical residential properties and optimizing performance. As an example, the time and power expenses related to each therapy produce a ripple result in producing efficiency and result. Annealing calls for cautious monitoring of temperature level and time to guarantee a valuable treatment without excessive over-softening, while normalizing, many thanks to quicker cooling times in air, frequently enables decreased downtime in manufacturing routines. Both processes call for cautious factors to consider not only for achieving ideal microstructure but additionally for integrating well within the assembly line, eventually impacting financial viability and sustainability.
Moreover, the complexities of annealing versus stabilizing discover importance in research and academic community, where a deeper understanding of products can lead to improvements in design practices. For example, in lightweight yet long lasting applications, such as automotive and aerospace parts, the strategic application of various warm therapies can significantly influence product option. Research study initiatives often study the results of both procedures and create optimized approaches that mix therapy strategies, permitting ingenious remedies that fulfill the ever-evolving needs of modern markets.
With growing recognition of sustainability and power performance within making procedures, initiatives are underway to decrease the eco-friendly impact of these typical approaches. Researchers and designers are proactively going after methods to make treatment methods greener, evaluating energy use throughout procedure cycles, and including eco-friendly power sources where possible.
In terms of home comparisons, annealed and normalized materials use unique advantages owing to their integral microstructural attributes. This divergence illuminates the fragile interplay in between microstructure and the final features of a material, making it imperative for specialists in metallurgy or design to review their choices with both techniques in mind.
As advancements in products science proceed to develop, the interaction between procedures affects the study and development of brand-new alloys and composites. Researchers are constantly checking out mixes and ingredients that modify thermal treatment procedures, leading to the style of sophisticated materials that show novel efficiency characteristics.
Summing up the distinctions between annealed and normalized steels conveys a remarkable narrative of basic science, practical application, and continuous technology in material researches. In recognizing these essential procedures within heat treatment, specialists rally a deeper understanding that serves not only their prompt roles however adds to broader development throughout markets. Whether it is supplying tools for much safer framework, creating effective vehicle components, or pioneering the design of products for the future, the study of annealing and normalizing will definitely be a cornerstone topic, connecting the expertise of materials, the technical experience of engineers, and the development of sector standards for many years ahead. As the complexities of the material globe will certainly always offer difficulties, the proficiency of annealing and normalizing processes will be vital, ensuring the strength and sustainability of crafted parts. Each approach contributes distinctively to our product landscape, and grasping their distinctions is vital for those that look for to master the areas of metallurgy and products science. Through these insights, we grow a future where the concepts rooted in these thermal therapies guide us toward innovative services and durable applications that reverberate throughout all fields of society, thereby solidifying the critical relevance of these procedures in our day-to-day lives.